Overview
Interventional Pulmonology (IP) is a specialty within pulmonary medicine. IP uses advanced methods to diagnose and treat patients with lung cancer, pleural diseases and airway disorders. The physicians perform advanced procedures to help patients experiencing respiratory symptoms and to ensure fast results.
What are the advantages of IP at UT Medical Center?
Interventional pulmonology services are provided on either an inpatient or outpatient basis. Patients can be evaluated in outpatient clinics in Knoxville or surrounding locations before being scheduled for procedures at the main hospital.
The University of Tennessee Medical Center is the leading hospital facility in the Knoxville area with the expertise in advanced diagnostic and the therapeutic modalities for procedural management of lung conditions. A team of interventional pulmonologists and thoracic surgeons also handles complex airway problems.
The IP program in Knoxville offer state-of-the-art procedures using the latest technological developments to diagnose and manage diseases of the lungs. These procedures include:
- Advanced Diagnostic Bronchoscopy
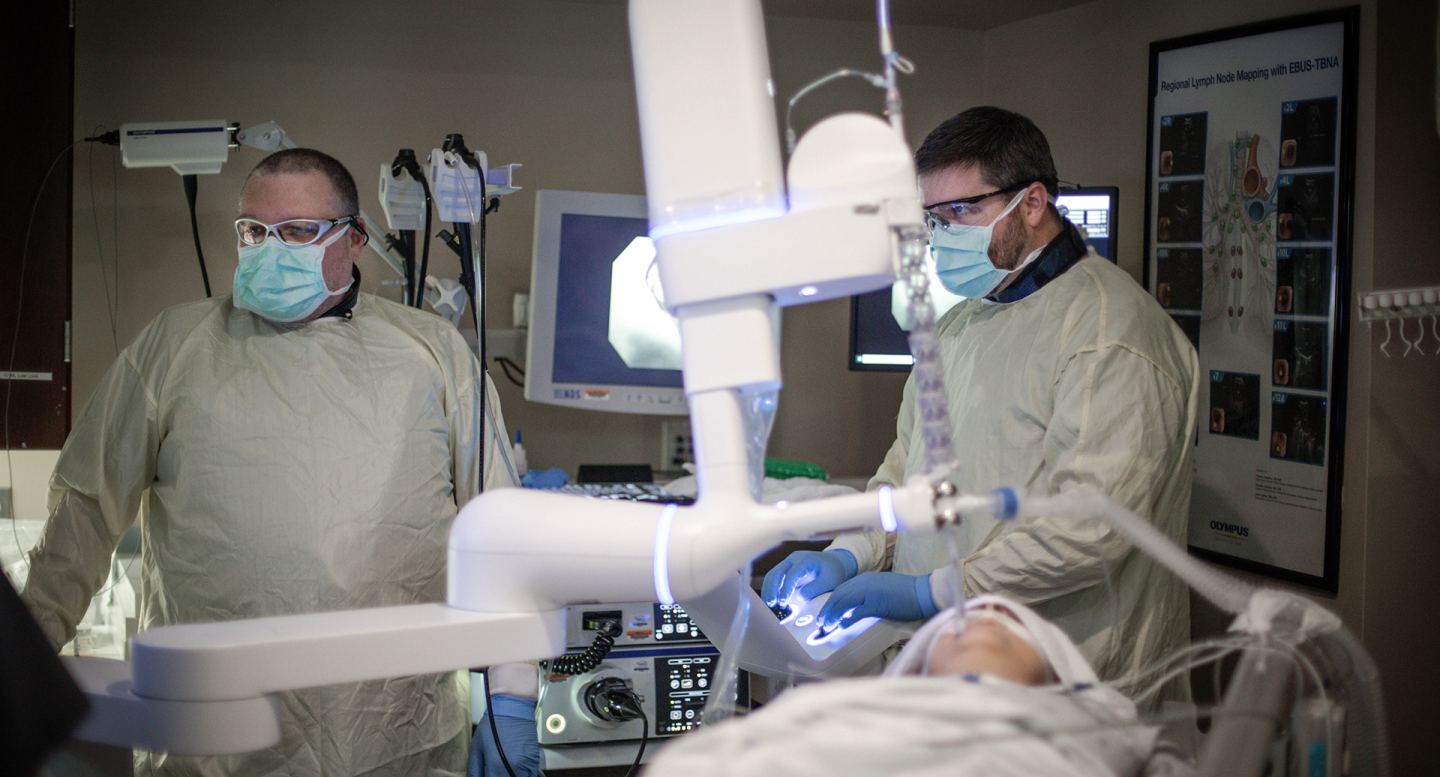
- Robotic Navigational Bronchoscopy
- Therapeutic Bronchoscopy - Destruction of airway tumor, Artificial airways
- Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction
- Pleural Disease Management
Advanced Diagnostic Bronchoscopy
Robotic navigational bronchoscopy is used to test or biopsy lesions in lungs that are too small or too difficult to reach using other, more common procedures. UTMCK uses a state-of-the-art robotic bronchoscopy platform in addition to real time intra-operative imaging using a CT scan to further increase the likelihood of obtaining a diagnosis.
Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) is a minimally invasive method of diagnosing lung cancer, infections, and other inflammatory diseases. EBUS enables doctors to obtain tissue or fluid samples from the lungs and surrounding lymph nodes. EBUS also provides real-time imaging of airways, blood vessels, lungs and lymph nodes to ensure safe sampling of lung tissue
Broncho-Alveolar Lavage (BAL) is a procedure where deep samples are obtained from the lung. This provides helpful information about different lung abnormalities and aids in diagnosis and treatment of infections, inflammatory lung conditions, etc
Pleural Disease Management
Thoracentesis and pleural biopsy removes fluid or air from the pleural space or body cavity surrounding the lungs. It is used to diagnose or treat diseases within the pleural cavity.
Chest tube with pleurodesis. removes fluid from the surrounding the lungs and prevents fluid from accumulating by instillation of approved agents in chest cavity.
Tunneled pleural catheter is an outpatient treatment to help prevent the recurrence of fluid accumulation around the lungs. Patients can drain fluid at the comfort of their home.
Placement of bronchial valves for bronchopleural fistula closure uses one-way valves to close an abnormal connection or passageway between organs or blood vessels (called a fistula) to reduce the air leaks and allows healing.
Therapeutic Bronchoscopy
Rigid bronchoscopy is when a bronchoscope is inserted into an airway through the nose or mouth to help doctors look for abnormalities like foreign bodies, bleeding, tumors, or inflammation that could be blocking the airway.
Percutaneous tracheostomy is a small incision is made in emergency to gain access to the trachea or windpipe. This is also performed to allow long term ventilator usage in patients with chronic respiratory failure. Team of physicians and nurses follow the patient with tracheostomy in the clinic for long term care.
Transtracheal oxygen catheter delivers oxygen directly to the lungs through a catheter or small, flexible tube that has been placed into the windpipe or trachea.
Therapeutic Bronchoscopy is relief of central airway obstruction caused by tumor or foreign object. Procedure performed under general anesthesia. Tumor is locally destroyed using specialized instruments that generate extreme heat or cold temperatures using electrocautery, argon plasma coagulation, laser or cryotherapy. The goal is immediate relief of airway stenosis.
Tracheal or bronchial dilation and stenting relieve difficult breathing due to the compression of windpipe by surround tumors or structures. Airway stents can be placed to keep the windpipe open and allow the patient to breath better.
Treatment of carcinoma in situ treats early forms of carcinoma by locally applied therapy, before the surrounding tissue is affected.
Treatment of trachea-bronchomalacia or other benign airway stenosis prevents excessive and abnormal airway collapse during breathing or coughing.
Placement of catheters for brachytherapy puts catheters or small flexible tubes in to treat different types of cancer.
Placement of fiducial markers for CyberKnife or Surgical removal puts fiducial markers that are points of reference or landmarks to help doctors target tumors for treatment.
Whole-lung lavage for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis puts one lung on a ventilator while the other lung is filled with saline and drained. This procedure helps clear out any materials clogging the air spaces in the lungs.